Spayed Female Dog Itchy Nipples: Spaying is a common and responsible procedure for pet owners that involves the removal of a female dog’s ovaries and uterus.
While it brings many health and behavioral benefits, some spayed dogs may experience certain issues post-surgery.
One such concern is itchy nipples. This article explores the potential causes, symptoms, and solutions for itchy nipples in spayed female dogs.
Spayed Female Dog Itchy Nipples: Understanding the Issue
Causes of Itchy Nipples in Spayed Female Dogs
1. Hormonal Imbalances
- Estrogen and Progesterone Levels: After spaying, the abrupt cessation of estrogen and progesterone production can lead to skin changes. Hormonal imbalances might make the skin around the nipples more sensitive and prone to itching.
- Thyroid Issues: Hypothyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones, which can affect the skin and coat, leading to dryness and itching.
2. Allergies
- Food Allergies: Certain ingredients in a dog’s diet, such as wheat, dairy, or specific proteins, can cause allergic reactions, including itchy skin around the nipples.
- Environmental Allergies: Pollen, dust mites, and mold are common allergens that can lead to skin irritation and itching in dogs.
3. Skin Infections
- Bacterial Infections: Skin folds around the nipples can harbor bacteria, especially in breeds with more skin folds. This can lead to infections and itchiness.
- Fungal Infections: Yeast infections can cause severe itching and discomfort, often appearing in warm, moist areas such as around the nipples.
4. Parasites
- Fleas and Ticks: These external parasites can cause intense itching. Fleas are particularly problematic because their bites can lead to flea allergy dermatitis, which exacerbates itching.
- Mites: Mange, caused by mites, can lead to severe itching and inflammation around the nipples.
5. Dermatitis
- Contact Dermatitis: Direct contact with certain materials, such as bedding, shampoos, or cleaning agents, can cause allergic reactions, leading to itchy nipples.
- Atopic Dermatitis: This is a chronic condition that can cause itching and inflammation in various parts of the body, including the nipples.
Symptoms of Itchy Nipples in Spayed Female Dogs
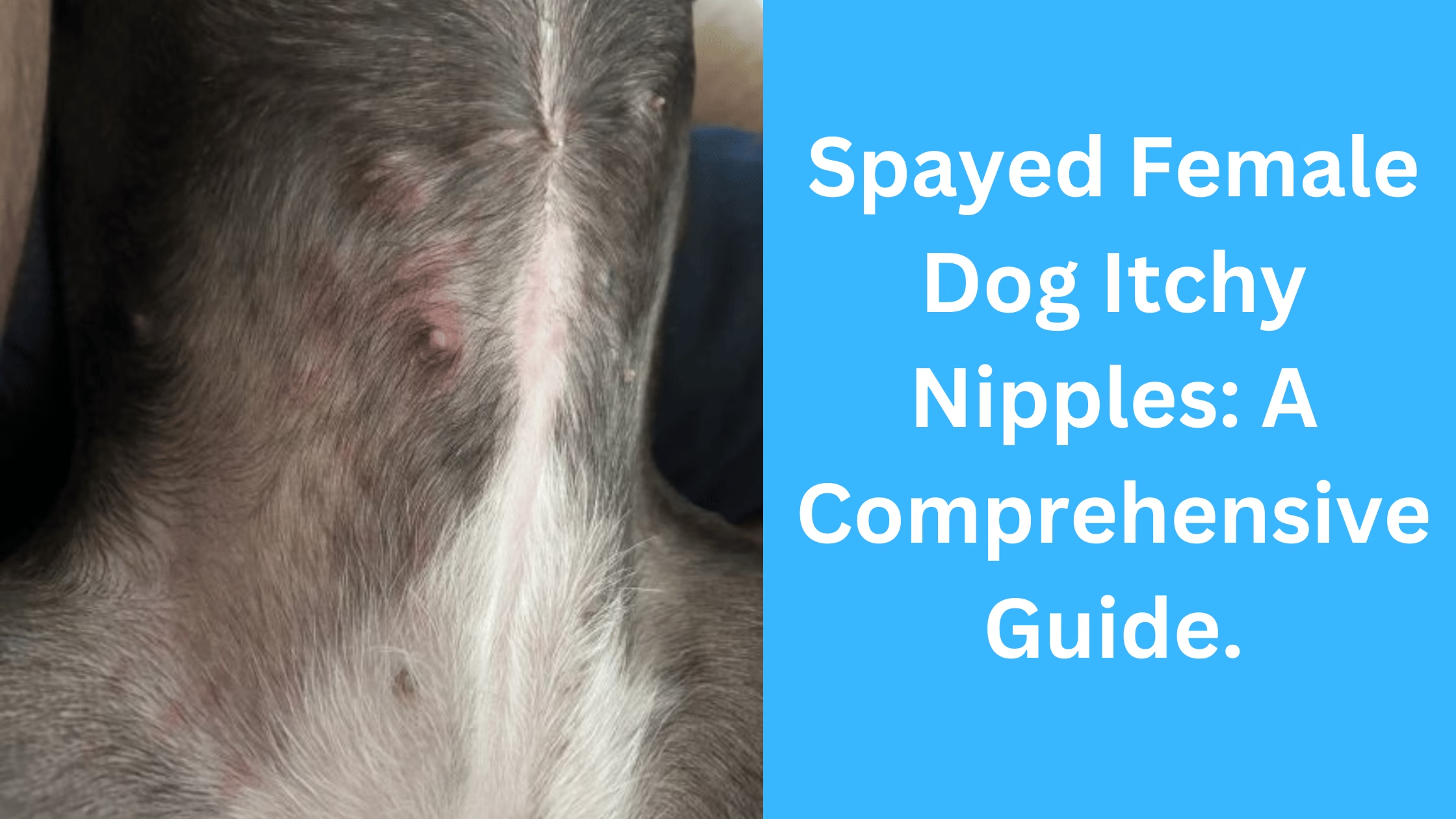
1. Visible Redness and Swelling
Inflammation and redness around the nipples are common signs of irritation. Swelling might also occur if the dog has been scratching or licking the area excessively.
2. Excessive Licking and Scratching
Dogs often lick or scratch itchy areas to try to alleviate the discomfort. If you notice your dog focusing on her nipples more than usual, it could indicate an issue.
3. Hair Loss
Persistent itching can lead to hair loss around the nipples. This can also be a sign of underlying conditions such as infections or parasites.
4. Scabs and Crusts
If the itching is severe, it might lead to the formation of scabs and crusts due to continuous scratching and licking.
5. Behavioral Changes
Discomfort from itchy nipples can cause changes in behavior, such as irritability, restlessness, or decreased interest in usual activities.
Diagnosis and When to See a Vet
1. Veterinary Examination
A thorough examination by a veterinarian is crucial to determine the cause of the itching. This includes checking the dog’s overall health, skin condition, and possibly conducting blood tests or skin scrapings.
2. Allergy Testing
If allergies are suspected, your vet might recommend allergy testing to identify specific triggers. This can include blood tests or intradermal skin tests.
3. Skin Biopsies and Cultures
For persistent or severe cases, a vet may take skin biopsies or cultures to diagnose infections or other underlying conditions accurately.
Treatment Options for Itchy Nipples
1. Topical Treatments
- Medicated Shampoos and Creams: These can help alleviate itching and treat infections. Ingredients like hydrocortisone and antifungal agents are often effective.
- Antihistamines and Steroids: These medications can reduce inflammation and itching. However, they should only be used under veterinary guidance.
2. Dietary Changes
- Hypoallergenic Diets: If food allergies are suspected, switching to a hypoallergenic diet can help. This involves eliminating common allergens and introducing novel proteins.
- Supplements: Omega-3 fatty acids and other supplements can improve skin health and reduce itching.
3. Flea and Tick Control
- Regular Treatment: Use vet-recommended flea and tick preventatives regularly to keep these parasites at bay.
- Environmental Control: Ensure your dog’s living environment is clean and free from fleas and ticks. Regular cleaning and vacuuming can help.
4. Hormone Therapy
- Thyroid Supplements: If hypothyroidism is diagnosed, hormone replacement therapy can be effective.
- Hormonal Treatments: In some cases, hormone therapy may be necessary to balance hormone levels and reduce itching.
5. Addressing Dermatitis
- Avoiding Irritants: Identify and remove any potential irritants from your dog’s environment.
- Moisturizing Agents: Use hypoallergenic moisturizing agents to keep the skin hydrated and reduce itchiness.
Home Care and Preventive Measures
1. Regular Grooming
Regular grooming helps keep your dog’s skin and coat healthy. It also allows you to check for signs of parasites or skin issues early.
2. Proper Nutrition
A balanced diet with essential nutrients supports overall health and can prevent skin issues. Consult your vet for dietary recommendations tailored to your dog’s needs.
3. Hygiene and Cleanliness
Keep your dog’s living area clean. Regularly wash bedding, toys, and other items your dog frequently uses.
4. Observation and Monitoring
Keep an eye on your dog’s behavior and skin condition. Early detection of changes can help in addressing issues before they become severe.
5. Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate skin conditions. Ensure your dog has a stress-free environment with plenty of physical and mental stimulation.
Also Read: NexGard Plus for Dogs: Complete Dog Parasite Protection
Also Read: Anise for Dogs (Dognip): A Comprehensive Guide
Conclusion
Itchy nipples in spayed female dogs can stem from various causes, including hormonal imbalances, allergies, infections, parasites, and dermatitis.
Understanding the symptoms and seeking timely veterinary care are crucial steps in addressing the issue.
With appropriate treatment and preventive measures, you can help ensure your dog remains comfortable and healthy.
If you notice any signs of discomfort in your dog, consult your veterinarian to determine the underlying cause and the best course of action.